CSCI 1200 - 作业 3 - 动态矩阵
作业要求
Details
直译
在这个作业中,你将构建一个名为 Matrix 的自定义类,该类将模仿传统的矩阵(matrix 的复数形式)。你不需要对矩阵有深入的了解,但如果你好奇,可以在线阅读更多内容:Matrix (mathematics)。
矩阵被用于许多不同的应用程序,多年来已经开发了许多优化、技巧和数值方法,以快速处理矩阵运算并解决更复杂的问题。
构建这个数据结构将帮助你练习指针、动态数组分配和释放、二维指针以及类设计。这个数据结构的实现将涉及编写一个新类。你不允许在实现中使用任何 STL 容器类,也不允许使用除 Matrix 之外的任何额外类或结构体。你需要使用 new 和 delete 关键字。你可以使用数组索引 []。在开始实现之前,请仔细阅读整个说明。
数据结构
矩阵是一个数字的二维排列。在这个作业中,我们将假设每个矩阵包含 doubles。我们用 m 行 n 列的矩阵来表示矩阵的大小。例如,下面展示的是一个 4×3 矩阵:
我们将使用二维数组来表示 Matrix 类中的数据。由于矩阵可以是任何大小,你需要使用动态内存来完成这个任务。上面的矩阵可以表示如下:
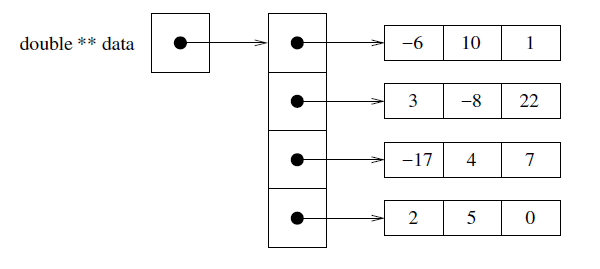
我们将用 表示矩阵 中第 行第 列的值。因此,一般矩阵可以描述为:
基础功能
你的类的私有部分会相当小,主要挑战在于在实现功能时处理动态内存。你可以按任何顺序实现这些方法;我们首先提到一些有助于调试的方法。
我们建议你首先编写一个构造函数,它接受两个 unsigned ints:行数和列数,以及一个 double 填充值。构造函数应创建一个行数×列数的矩阵,每个值都初始化为填充值。如果任一维度为 0,则结果矩阵应为 0×0。
你的类必须支持等于运算符 == 和不等于运算符 !=。如果两个矩阵在每个位置的值都相同,则它们被认为是相等的。换句话说,矩阵 A 和 B 相等当且仅当
是“对于所有”的常见缩写,所以 表示“对于每个 i 和 j 的值”。 是“在…中”的常见缩写。
由于矩阵有两个维度,你需要实现 num_rows() 和 num_cols() 方法,分别返回矩阵的行数和列数。我们可能需要将一个已填充的矩阵改为一个空矩阵,因此你必须编写 clear() 方法。该方法应将行数和列数重置为 0,并释放 Matrix 当前持有的任何内存。
自然地,我们需要能够访问 Matrix 类中存储的数据。为此,我们将实现一个“安全”的访问器叫做 get(),它接受一个 row、一个 column 和一个 double。如果行和列在矩阵的范围内,则 arow,col 的值应存储在 double 中,并且函数应返回 true。否则函数应返回 false。
与访问数据类似但互补的任务是能够设置矩阵中特定位置的值。这通过一个安全的修改器 set() 来完成。这个函数也接受 row、column 和一个 double 值。如果位置超出范围,set() 返回 false,如果位置有效则返回 true。如果位置有效,函数还应将 arow,col 设置为传入的 double 值。
重载输出运算符
在某个时候,编写一个输出方法可能是个好主意。与之前我们编写一个打印方法的类不同,我们将依赖一个非成员的 operator<< 重载。我们之前练习过为 std::sort() 调用重载其他运算符,这与此类似。在 Matrix 类定义之外,但仍在你的 .cpp 和 .h 文件中,你应该编写以下 operator:
|
|
这将允许我们顺序打印一个或多个输出。如果你的 operator<< 实现正确,以下所有代码都应该可以运行:
|
|
让我们假设在上面的例子中:
那么输出应该类似如下:
|
|
我们将忽略空格,但期望你的运算符输出矩阵的元素顺序正确,大小输出在矩阵之前,并且遵循以下格式 - 每行一个矩阵,元素之间有空格。请注意,即使在这些例子中,对齐也不是很理想。我们更希望你专注于正确实现 Matrix 类和处理内存,而不是让输出看起来美观。
简单的矩阵操作
首先,我们介绍一些基本的矩阵操作。第一个是 multiply_by_coefficient() 方法,它接受一个名为 coefficient 的 double。该方法应将矩阵中的每个元素乘以 coefficient。例如:
另一个常见的操作是交换矩阵的两行。这将通过 swap_row() 方法完成,它接受两个类型为 unsigned int 的参数:源行号和目标行号。如果两行都在矩阵的范围内,则函数应交换两行的值并返回 true。否则函数应返回 false。例如:
注意
在完成基本功能和 swap_row() 之后,可以调用 matrix_main.cpp 中提供的 rref() 函数的测试。我们在这里不详细解释该函数,你不需要知道它如何工作,但计算简化行阶梯形式(RREF)可以用来找到逆矩阵,这在许多领域都很重要。我们使用一种简单实现的方法叫做高斯-约旦消元法(Gauss-Jordan Elimination),你可以在这里阅读:Gaussian elimination。还有其他寻找 RREF 的方法更好,但我们选择这种方法是因为它简单。
“翻转”矩阵是常见的需求,这个过程叫做转置(transposition)。你需要编写 transpose() 方法,返回类型为 void。形式上,将 m×n 矩阵 A 转置为 n×m 矩阵 A^T 定义为:
二元矩阵操作
二元矩阵操作是指涉及两个矩阵的操作。为了保持简单,我们将它们写成方法(不是运算符),这些方法位于类定义内部,因此当前 Matrix 对象将始终是“左操作数”矩阵 A。你需要实现 add() 和 subtract() 两个函数。这两个函数只接受一个参数,即第二个矩阵,我们称之为 B,并在 A 和 B 的维度匹配时修改 A。如果维度匹配,函数应返回 true,否则返回 false。两个矩阵的加法,C = A + B,和两个矩阵的减法,D = A − B,形式上定义为:
考虑以下两个矩阵:
更复杂的矩阵操作
如果我们想要获取整行或整列的内容,使用 get() 一个一个提取值会很麻烦,尤其是由于我们的实现是一个“安全”的访问器,我们不能使用一些常规的编码技巧。为了解决这个问题,你需要实现两个额外的访问器 get_row() 和 get_col()。这两个函数都接受一个 unsigned int 并返回一个 double*。对于 get_row(),参数是要检索的行号,而对于 get_col(),参数是要检索的列号。如果请求的行或列超出矩阵范围,该方法应返回一个指向 NULL 的指针。
我们期望你实现的最后一个方法是 quarter(),这不是传统的矩阵操作。该方法不接受任何参数,返回一个 Matrix*,其中包含四个新的 Matrix 元素,顺序为:左上(UL)象限、右上(UR)象限、左下(LL)象限,最后是右下(LR)象限。所有四个象限的大小应该相同。记住,当一个函数结束时,所有局部变量都会超出作用域并被销毁,因此你需要特别注意如何构造和返回这些象限。下一页展示了两个 quarter 操作的例子:
测试和调试
我们提供了一个 matrix_main.cpp 文件,其中包含 Matrix 类的大量测试。其中一些测试最初被注释掉了。我们建议你先让类在基础测试中运行,然后在实现和调试剩余功能时取消注释其他测试。研究提供的测试用例以了解参数和返回值。
注意:不要编辑提供的 matrix_main.cpp 文件,除非在实现过程中取消注释提供的测试用例,以及在指定位置添加你自己的测试用例。
assert() 函数在测试代码中广泛使用。这是一个在 C 和 C++ 中都可用的函数,如果条件为真则什么也不做,如果条件为假则会立即崩溃。如果条件为假,你的命令行应该显示在崩溃前失败的断言。
我们建议使用内存调试工具来查找内存错误和内存泄漏。有关安装和使用内存调试工具“Dr. Memory”(适用于 Linux/MacOSX/Windows)和“Valgrind”(适用于 Linux/OSX)的信息在课程网页上:http://www.cs.rpi.edu/academics/courses/fall23/csci1200/memory_debugging.php
作业提交服务器也将使用 Dr. Memory 运行你的代码以查找内存问题。你的程序必须没有内存错误和内存泄漏才能获得满分。
你的任务与提供的代码
你需要按照说明实现 Matrix 类。你的类应该在 .cpp 和 .h 文件之间进行划分。你还需要在 matrix_main.cpp 的 StudentTest() 函数中包含一些额外的测试。在实现类时,请特别注意正确实现复制构造函数、赋值运算符和析构函数。
在实现类时,请注意返回类型、const 关键字和按引用传递。如果你正确实现了 Matrix 类,那么运行提供的 matrix_main.cpp 文件与你的类,应该产生 sample_output.txt 中提供的输出。我们对空格的差异不太挑剔,但你应该努力尝试匹配我们的输出和你的输出之间的空格和换行符。
提交
你需要提交 matrix_main.cpp、Matrix.cpp、Matrix.h 和 README.txt 文件。请注意,Submitty 将使用 instructor 的 matrix_main.cpp 文件进行大部分测试,因此你必须确保你的 Matrix 实现可以与提供的文件编译。同时,确保你的类实现文件名称使用大写字母,因为 Linux 是区分大小写的。
确保编写你自己的新测试用例,并不要忘记注释你的代码!使用提供的模板 README.txt 文件来写你希望评分者阅读的笔记。在 README.txt 文件中填写顺序表示部分。你必须按照“Collaboration Policy & Academic Integrity”说明独立完成这个作业。如果你与任何人讨论了这个作业、解决问题的方法或错误信息等,请在 README.txt 文件中列出他们的名字。
截止日期: 02/06/2025,星期四,晚上 10 点。
评分标准
20 分
- README.txt 完成(3 分)
- 未填写姓名、合作者或工作时间中的一个。(-1)
- 未填写姓名、合作者或工作时间中的两个或更多。(-2)
- 没有反思内容。(-1)
- 整体类声明与实现及编码风格(良好的类设计,分为 .h 和 .cpp 文件。函数超过一行的放在 .cpp 文件中。类实现组织良好,注释合理。正确使用 const/const& 和类方法的 const。)(5 分)
- 无分数(实现明显不完整)(-5)
- 没有为 Matrix 提供文档(函数文档和部分标题不算)。(-1)
- 函数体包含超过一条语句的放在 .h 文件中。(对于模板类是允许的)(-2)
- 函数没有充分文档或在 .h 或 .cpp 文件中注释不佳。(-1)
- const 和引用的使用不当或遗漏。(-1)
- 代码过于紧凑、空格过多或缩进不当。(-1)
- 变量名选择不当:不具描述性的名称(例如 ‘vec’, ‘str’, ‘var’)、单字母变量名(除了单个循环计数器)等。(-2)
- 数据表示(4 分)
- 无分数(实现明显不完整)。(-4)
- 使用 STL 数据结构(列表、向量等)。(-4)
- 成员变量是公共的。(-2)
- 顺序表示(README 包含正确的顺序表示分析,包括正确的表示和变量的使用)(5 分)
- 额外的测试用例(大量学生编写的额外测试用例)(4 分)
- 没有测试
transpose()。(-1) - 没有测试
multiply_by_coefficient()。(-1) - 没有测试
get_col()。(-1) - 没有测试某些类型的边界情况(行数或列数为 0,奇数维度的 quarter 操作等)。(-1)
- 没有测试用例,或者只是测试了 SimpleTests 中已涵盖的内容。(-4)
- 没有测试
支持文件
matrix_class.7z程序设计
首先,我们需要确定 Matrix 类的设计。根据提供的信息,我制作了一个图。
classDiagram
class Matrix {
%% Data members
- rows : unsigned int
- cols : unsigned int
- data : double**
%% Private Methods
- allocateMemory()
- deallocateMemory()
%% Constructors
+ Matrix()
%% Destructor
+ ~Matrix()
%% Public Methods
+ operator=()
+ get_rows() // 更改为 get_rows 和 get_cols,符合中文习惯
+ get_cols()
+ clear()
+ get()
+ set()
+ multiply_by_coefficient()
+ swap_row()
+ transpose()
+ add()
+ subtract()
+ get_row()
+ get_col()
+ quarter()
+ operator==()
+ operator!=()
%% Friend Operator
+ operator<<()
}
classDiagram
class Matrix {
%% Data members
- rows : unsigned int
- cols : unsigned int
- data : double**
%% Private Methods
- allocateMemory()
- deallocateMemory()
%% Constructors
+ Matrix()
%% Destructor
+ ~Matrix()
%% Public Methods
+ operator=()
+ get_rows() // 更改为 get_rows 和 get_cols,符合中文习惯
+ get_cols()
+ clear()
+ get()
+ set()
+ multiply_by_coefficient()
+ swap_row()
+ transpose()
+ add()
+ subtract()
+ get_row()
+ get_col()
+ quarter()
+ operator==()
+ operator!=()
%% Friend Operator
+ operator<<()
}踩坑内容
- 矩阵的大小不一定总是奇数。因此,当处理接近边缘的情况时需要额外努力。
- 我们需要编写一些测试用例,并且这些用例将由隐藏自动评分器进行测试。
解决方案
Matrix.h
|
|
Matrix.cpp
|
|
matrix_main.cpp(包含更多测试用例)
|
|
相关内容
- CSCI 1200 - 作业 2 - 设计一个简单的 Uber
- CSCI 1200 - 作业 1 - Spotify播放列表
- CSCI 1100 - 作业 8 - 熊、浆果与游客重聚:类
- CSCI 1100 - 作业 7 - 字典
- CSCI 1100 - 作业 6 - 文件、集合和文档分析